The numbers paint an ugly picture. 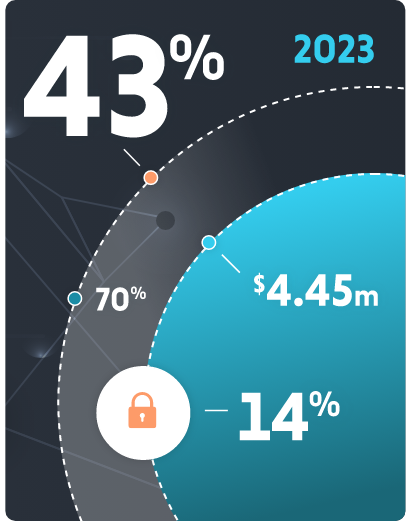
According to a study, 43% of today’s cyber attacks are aimed at small and medium-sized businesses. And yet, just 14% of those businesses are capable of defending their networks and data.
This is a major problem — not just for businesses targeted by cyber criminals, but also for the economy as a whole. Research from IBM finds that the average cost of a data breach reached an all-time high of $4.45 million in 2023. And a recent report from Apple and MIT found that in the first three quarters of last year alone, ransomware attacks increased by nearly 70%.
In short, stealing data is big business — and getting bigger. At the same time, access points to data have never been more prevalent — or vulnerable.
Given all this, it’s critical for businesses of all sizes to invest in data encryption.
What encryption does
While the most obvious use of data encryption is to keep private information private, it’s not the sole reason a business should invest in it. Other use cases include:
Keeping cybercriminals at bay: In the unfortunate event of a data breach, encrypted data remains useless to cyber criminals. This reduces the potential damage and limits the exposure of sensitive information.
Meeting compliance needs: Many regulatory frameworks, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), require organizations to protect sensitive data through encryption. A failure to do so can lead to legal repercussions and hefty fines.
Making data transmissions secure: Encryption is vital for securing data during transmission over networks. It prevents eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks, ensuring data reaches its intended recipient intact and confidential.
Keeping customer loyalty: Customers are more likely to trust organizations that take data security seriously — so much so that having a reputation for secure handling of data is often a differentiator when it comes to keeping customers loyal.

Current data encryption best practices
What does investing in data encryption look like?
Security measures are always evolving — as are the tactics of criminals — but there are some current best practices every business should follow. At Dynamic Computing, we regularly recommend:
Implementing strong encryption algorithms like Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) and/or Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA)
Following proper key management to ensure encryption keys are generated securely, stored in a protected environment, and regularly rotated
Employing hardware security modules (HSMs) to safeguard keys from unauthorized access
Utilizing end-to-end encryption for sensitive communications and data storage
Properly classifying data based on its sensitivity so you can allocate resources effectively
Conducting regular auditing and monitoring to spot potential vulnerabilities
Combining encryption with multi-factor authentication (MFA) to require users to provide multiple forms of authentication
Beyond these important technical steps, one of the most critical areas to focus on is security education for employees. Human errors remain a leading cause of data breaches, and regular training can go a long way toward ensuring data stays safe across its lifecycle.
The role of IT
IT providers and departments play a central role in implementing and maintaining data encryption practices within organizations. The long list of responsibilities include:Infrastructure selection
IT professionals are responsible for choosing the appropriate hardware and software solutions for data encryption. This includes selecting encryption tools, cryptographic libraries, and hardware security modules (HSMs) to protect encryption keys.Encryption configuration
IT teams configure encryption settings for various applications, databases, and storage systems. They ensure that encryption is properly implemented and encryption keys are securely stored.Key management
Managing encryption keys is a critical task for IT departments. They generate, store, rotate, and monitor encryption keys to prevent unauthorized access.Security patching
Keeping encryption software and hardware up to date is essential. IT professionals regularly apply security patches and updates to protect against known vulnerabilities.Incident response
In the event of a data breach or security incident, IT teams play a vital role in containing the breach, assessing the impact, and coordinating the response, including the potential decryption of affected data if necessary.Compliance and auditing
IT departments ensure that encryption practices comply with relevant regulations and industry standards. They participate in security audits and assessments to validate compliance.Employee training
IT professionals collaborate with human resources and security teams to provide training and awareness programs for employees. They ensure that all staff understands the importance of data encryption and follows best practices.Monitoring and reporting
IT teams continuously monitor encrypted data and network traffic for signs of intrusion or suspicious activities. They generate reports and alerts for potential security threats.Disaster recovery
IT departments develop and maintain data recovery and backup strategies to ensure data can be restored in the event of a breach or data loss. Encryption plays a role in securing backups as well.
Always be prepared
From sensitive personal information to critical business data, the need for data security has never been greater.
That makes data encryption a fundamental component of any operation's cyber security approach — a component that lands on the shoulders of IT.
Cyber criminals aren’t going anywhere. In fact, their methods are only going to get more creative and sophisticated. But with proper data encryption in place, businesses can successfully thwart attacks before they inflict damage. That makes it a very sound investment.

